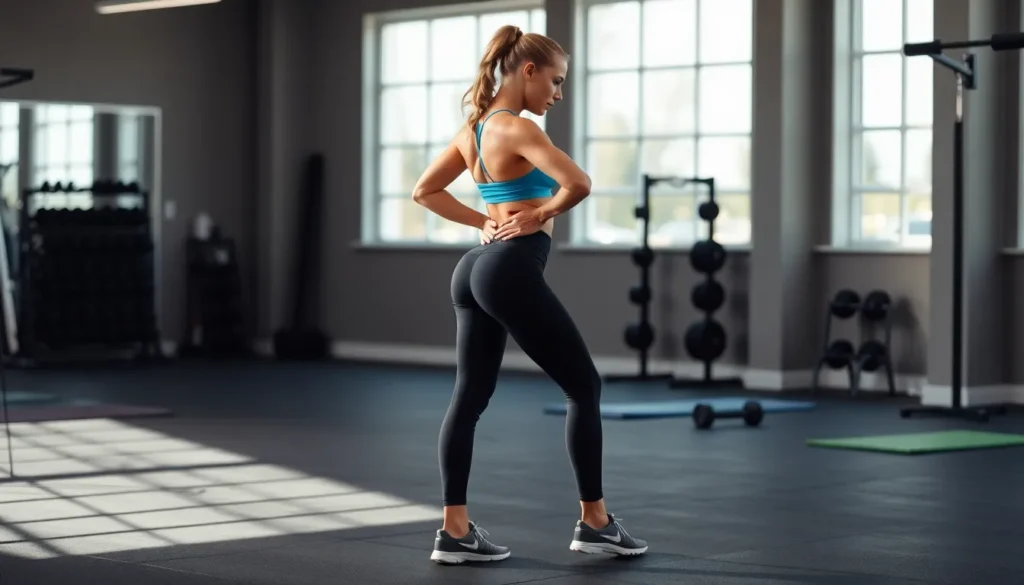
The hip hinge exercise might sound like a fancy dance move, but it’s actually a game-changer for anyone looking to boost their fitness routine. This simple yet powerful movement targets the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back, making it a must-have in any workout arsenal. Forget about those awkward squats that leave you feeling like a pretzel; mastering the hip hinge can unlock a world of strength and stability.
Hip Hinge Exercise
The hip hinge exercise is a fundamental movement pattern that’s crucial for many fitness routines. This exercise specifically targets muscle groups like the glutes, hamstrings, and lower back.Definition and Purpose
The hip hinge involves bending at the hips while keeping a neutral spine. This action allows for effective engagement of major muscle groups during various physical activities. Practicing the hip hinge helps improve posture and enhance athletic performance. Many trainers integrate it into strength training routines because it lays the foundation for functional movements.Importance in Strength Training
Strength training benefits significantly from the hip hinge movement. Incorporating this exercise increases overall strength and stability in the lower body. As individuals master the hip hinge, they develop better lifting mechanics, reducing the risk of injury during heavy lifts. Enhanced core engagement during the hip hinge leads to stronger and more resilient muscles. Many athletes rely on this exercise to improve their performance in sports that require explosive lower body strength.Benefits of the Hip Hinge Exercise
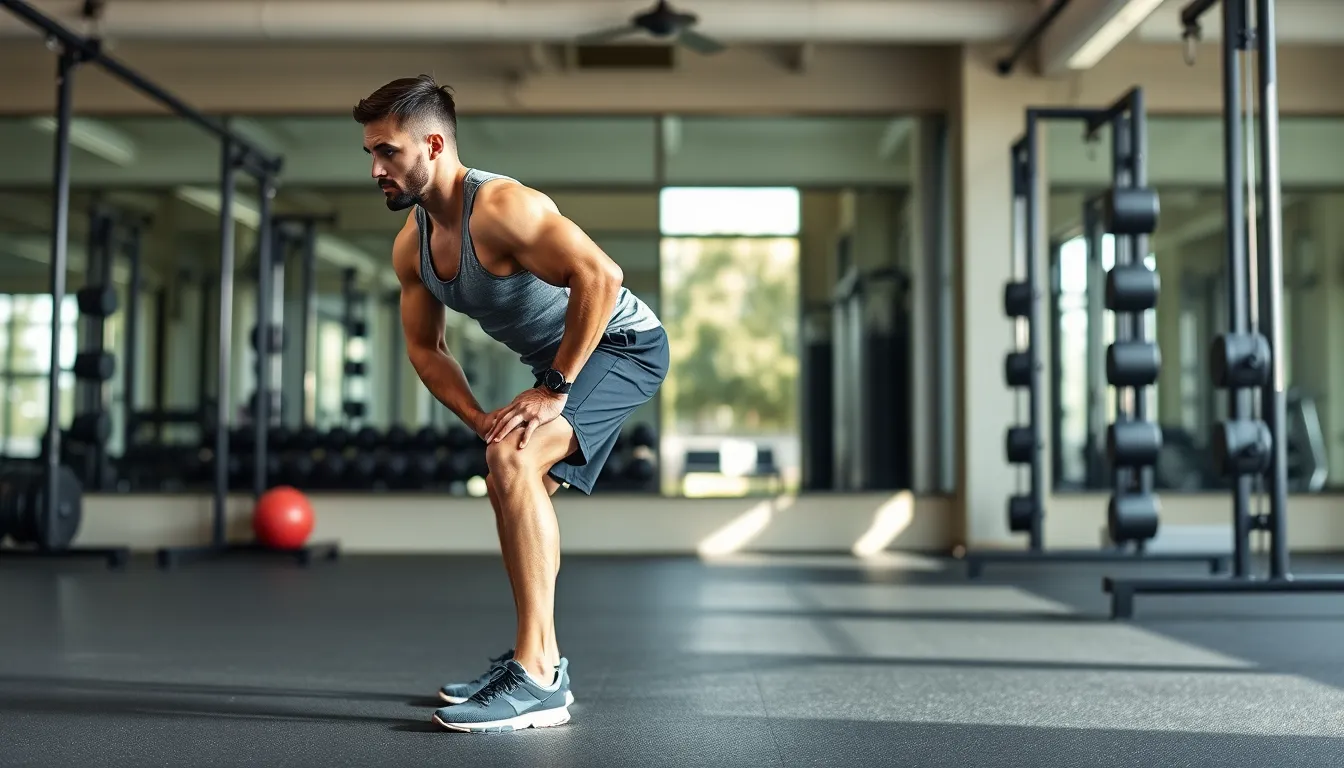

Improves Posterior Chain Strength
Strengthening the posterior chain significantly enhances athletic capability. The hip hinge effectively engages the glutes and hamstrings. Increased activation of these muscles leads to better overall power during movements. Improvements in lower back strength also occur, which supports proper lifting mechanics. Enhanced strength in the posterior chain is vital for athletes, as it improves performance in sports requiring sprinting or jumping. Training these muscle groups with the hip hinge translates to more effective lifts in other exercises.Enhances Mobility and Flexibility
Mobility and flexibility gain from the hip hinge exercise are essential for functional movement. This exercise encourages proper hip hinge mechanics while maintaining a neutral spine. Improved range of motion in the hips leads to better overall athletic performance. Regular practice promotes flexibility in the hamstrings, reducing tightness. As the hip hinge develops strength and flexibility, it assists in maintaining proper posture during dynamic activities. Enhanced mobility helps reduce the risk of injury during sports and daily movements, making the hip hinge invaluable for diverse training regimens.How to Perform the Hip Hinge Exercise
Executing the hip hinge correctly maximizes its effectiveness. Focus on these key steps to ensure proper form.Step-by-Step Instructions
-
- Stand tall with feet hip-width apart and weight distributed evenly.
-
- Keep the chest proud and shoulders back to maintain a neutral spine.
-
- Push the hips back while bending at the hips, allowing a slight bend in the knees.
-
- Lower the torso until it’s almost parallel to the floor but maintain a flat back.
-
- Engage the glutes and hamstrings to return to the starting position by driving the hips forward.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
- Avoid rounding the back; it compromises spinal integrity.
-
- Don’t let the knees excessively extend forward; this shifts the focus from the hips.
-
- Keep the head in a neutral position; don’t look too far up or down.
-
- Don’t rush the movement; control is essential for effectiveness.
-
- Avoid lifting too heavy too soon; focus on mastering form first.